Implementation strategies
Coordinator-based Systems for Secondary Prevention in Fragility Fracture Patients
Summary
Scientific evidence shows that a coordinated, multi-disciplinary approach to patient care is the most clinically and cost-effective in preventing secondary fractures. A systematic approach to secondary fracture prevention can result in fewer fractures and significant cost savings to healthcare systems. The IOF Working group has published an important review outlining the evidence.
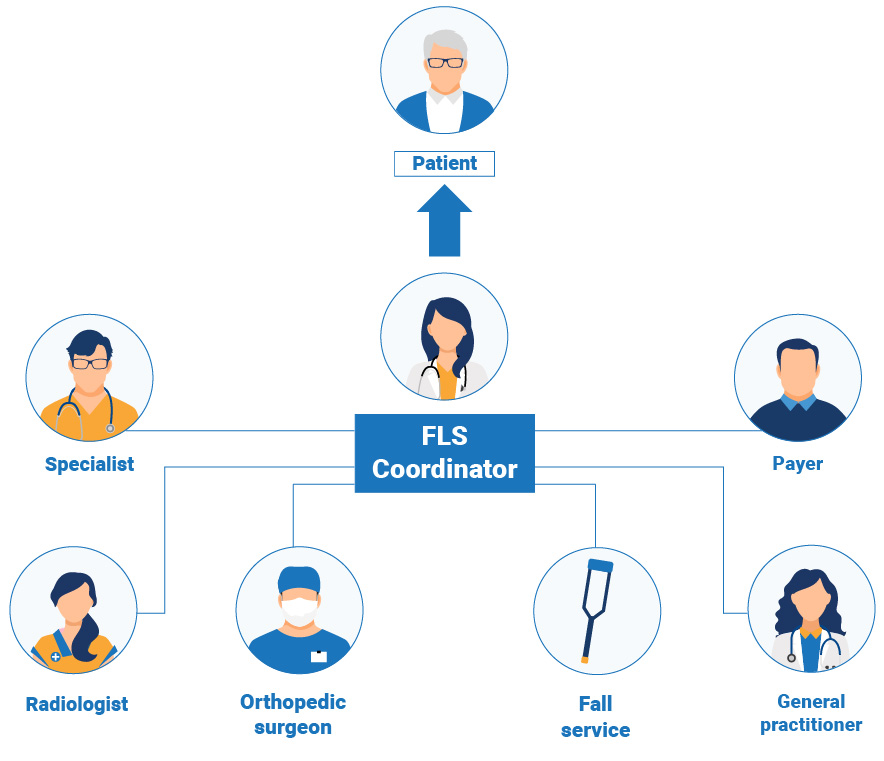
The key steps to implementation described in the review are:
1. Get the team together
2. Create a service development team, headed by a champion, which is likely to include:
- Lead clinician/local champion
- Secondary care clinicians - consultant orthopaedic surgeon, consultant radiologist, consultant geriatrician
- Nurse specialists/practitioners (if and when appointed)
- Local primary care providers
- Patient representatives
- Allied health professionals e.g, physiotherapists
- Consultants in Public Health
- Service/business managers for institution/locality
- Community-based pharmacists
- Hospital / local community prescribing management team member
3. Secure access to post-fracture patients
4. Estimate the workload and resources needed
5. Define the role of the post-fracture coordinator
6. Build a business case
- IOF has developed a generic FLS business plan template for use when engaging with local planning machinery.
7. Engage with the local planning machinery
8. Start prospective data collection
9. Initiate the service and develop it iteratively
Rapid cycle process improvement methods have been central to the development of successful coordinator-based, post-fracture models of care throughout the world. This method applies sequential Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles, details of which are available in a publication from the United States:
11 Key Performance indicators to the broad patient pathway following a fragility fracture
Read full paper at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00198-020-05377-1
Summary
The IOF Capture the Fracture® Working Group, with the National Osteoporosis Foundation and the Fragility Fracture Network, has developed 11 patient-level performance indicators to measure FLS effectiveness and guide quality improvement.
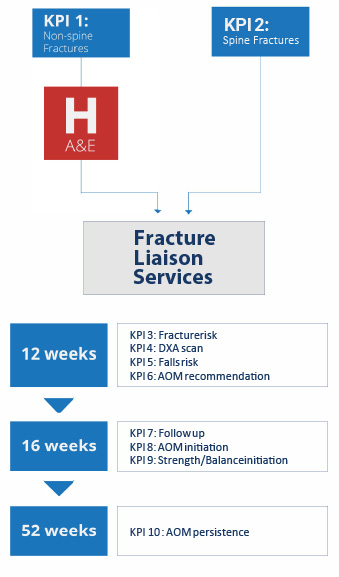
Mapping the 11 key performance indicators to the broad patient pathway following a fragility fracture
FLS often operate in complex local healthcare systems relying on the effective interplay between people, equipment, processes and institutions as well as competing priorities, resources and reimbursement.
The Capture the Fracture Best Practice Framework standards are helpful for identifying major gaps in the service delivery such as types of patients with fractures identified and presence of monitoring. However they are less helpful for helping established FLS reach their full potential for secondary fracture prevention in the context of local challenges and opportunities. We here present a complimentary key performance indicator (KPI) set that measures the real-world secondary fracture prevention delivery at the patient level. The objective of these KPIs is to demonstrate areas for service improvement and measure the impact of service interventions within a plan-do-study-act methodology, the building blocks of iterative healthcare improvement.
Identifying Patients
Nature has provided us with an opportunity to systematically identify almost half of individuals who will break their hip in the future... through identifying those who experience a fragility fracture today. This is why implementation of FLS is crucial.
The pyramid below illustrates the populations that can be targeted for fracture risk assessment from the perspective of ease of case-finding. Patients presenting to hospital Emergency Departments or community-based fracture clinics with new fragility fractures are the most readily identifiable group
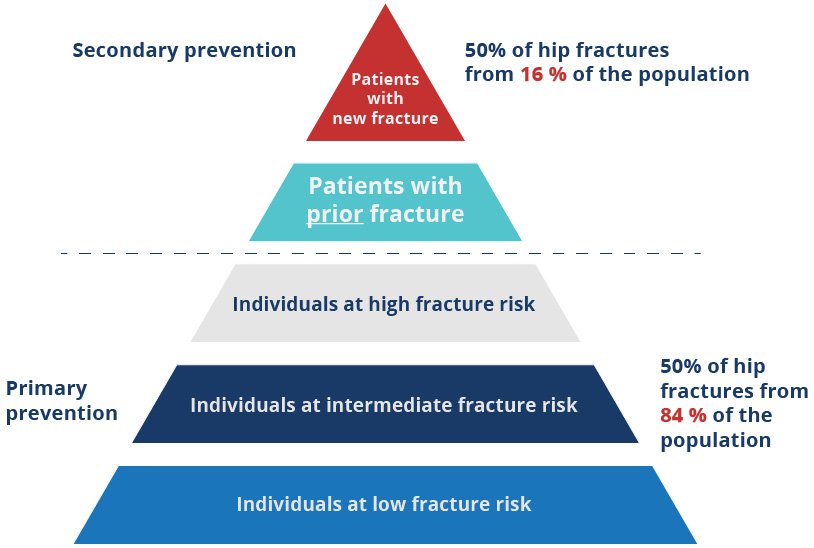
“Mitchell PJ. Fracture Liaison Services: the UK experience. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22 Suppl 3:487-494. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1702-2”
The next level of the pyramid – patients with prior fracture – refers to those patients that have suffered a fragility fracture in the past. In the absence of a system being in place at the time that the prior fractured occurred, assessment for osteoporosis will probably not have been done.
These prior fracture patients could be identified for fracture risk assessment if hospital or community-based fracture clinics maintain electronic patient records. Alternatively, in countries with established primary care infrastructure, the patient’s general practitioner could also hold information on prior fracture history.
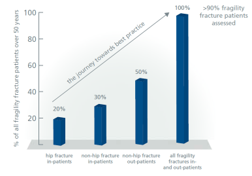
In order to implement an effective systems-based approach to secondary prevention for individuals presenting to urgent care services with new fragility fractures, the scope of such a service must be clearly defined from the outset. The graph on the right provides a context to consider which groups of fracture patients should be targeted. Some of the established FLS models began by targeting just hip fracture patients.
The scope was subsequently expanded to include all patients admitted to hospital and, finally, all patients managed in the outpatient fracture clinic setting. Other services aimed for total patient capture from the outset.
In localities which currently lack a systematic approach to case-finding individuals with new fragility fractures, it is likely that patients who have fractured in the past have not received osteoporosis assessment or treatment. Case-finding of prior fragility fracture patients could be conducted electronically where electronic patient management systems have fracture data coded in a reliable fashion. If such electronic searches are not possible, questionnaires targeted to older adults provide a means to conduct retrospective case-finding. A publication from the UK highlights a successful illustration of this approach:
Closing the osteoporosis management gap in primary care: a secondary prevention of fracture programme. Brankin E, Mitchell C, Munro R; Lanarkshire Osteoporosis Service. Curr Med Res Opin. 2005 Apr;21(4):475-82. PubMed ID 15899094